3.3.2.2. init_task
linux下有三个特殊的进程,idle进程(PID=0) init进程(PID=1)和 kthreadd(PID=2)
idle进程是系统自动创建,运行在内核态
idle进程其pid=0,其前身是系统创建的第一个进程,也是唯一一个没有通过fork或者kernel_thread产生的进程。完成加载系统后,演变为进程调度、交换
init进程由idle通过kernel_thread创建,在内核空间完成初始化后,加载init程序,并最终在用户空间运行
由0进程创建,完成系统的初始化,时系统中所有其他用户进程的祖先进程.linux中所有进程都是Init进程创建并运行的,首先linux内核启动,然后在用户空间启动Init进程,再启动其他系统进程. 在系统启动完成后,init将变为守护进程监视系统其他进程
kthreadd 进程由idle通过kernel_thread创建,并始终运行在内核空间,负责所有内核线程的调度和管理
它的任务就是管理和调度其他内核线程,会循环执行一个kthread的函数,该函数的作用就是运行kthread_create_list全局链表维护的kthread,当我们调用kernel_thread创建的内核线程 就会被加入到此链表中.因此所有的内核线程都直接或者间接的以kthreadd为父进程
3.3.2.2.1. idle的创建
在smp系统中,每个处理器单元有独立的运行队列,而每个运行队列上又有一个idle进程,即有多少个处理器单元就有多少个idle进程
系统的空闲时间,其实就是指idle进程的运行时间
3.3.2.2.1.1. 0号进程上下文信息-init_task描述符
init_task 是内核中所有进程、线程的task_struct雏形,在内核的初始化过程中,通过静态定义构造处理一个task_struct接口,取名为init_task,然后在初始化的后期,通过 rest_init() 函数创建了
内核init线程,kthreadd内核线程
内核init线程,最终执行/sbin/init进程,变为所有用户态程序的根进程(pstree命令显示),即用户空间的init进程.开始的init是由kernel_thread创建的内核线程.在完成初始化工作后,转向用户空间,并且生成所有用户进程的祖先
内核kthreadd线程,变为所有内核态其他守护线程的父线程
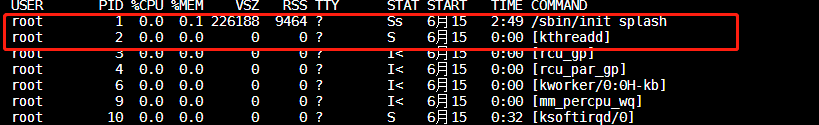
所以init_task决定了系统所有进程、线程的基因,它完成初始化后,最终演变为0号进程idle,并且运行在内核态
idle进程的优先级为MAX_PRIO-20,早期的版本中idle是参与调度的,但是目前的版本中idle并不在运行队列中参与调度,而是在运行队列结构中含idle指针,指向idle进程,在调度器发现运行队列为空的时候运行.
内核中的init_task变量就是进程0使用的进程描述符,也是linux系统中第一个进程描述符.
init_task 在init/init_task.c中定义
/*
* Set up the first task table, touch at your own risk!. Base=0,
* limit=0x1fffff (=2MB)
*/
struct task_struct init_task = {
.thread_info = INIT_THREAD_INFO(init_task),
.stack_refcount = REFCOUNT_INIT(1),
.state = 0,
.stack = init_stack,
.usage = REFCOUNT_INIT(2),
.flags = PF_KTHREAD,
.prio = MAX_PRIO - 20,
.static_prio = MAX_PRIO - 20,
.normal_prio = MAX_PRIO - 20,
.policy = SCHED_NORMAL,
.cpus_ptr = &init_task.cpus_mask,
.cpus_mask = CPU_MASK_ALL,
.nr_cpus_allowed= NR_CPUS,
.mm = NULL,
.active_mm = &init_mm,
.restart_block = {
.fn = do_no_restart_syscall,
},
.se = {
.group_node = LIST_HEAD_INIT(init_task.se.group_node),
},
.rt = {
.run_list = LIST_HEAD_INIT(init_task.rt.run_list),
.time_slice = RR_TIMESLICE,
},
.tasks = LIST_HEAD_INIT(init_task.tasks),
...
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(init_task);
3.3.2.2.1.2. 进程堆栈init_thread_union
init_task进程使用 init_stack作为进程堆栈
.stack = init_stack,
3.3.2.2.1.3. 进程内存空间
init_task的虚拟地址空间,也采用同样的方法定义
由于init_task是一个运行在内核空间的内核线程,因此其虚拟地址段mm为NULL,但是必要时它还是需要使用虚拟地址的,因此active_mm被设置为 init_mm
- ::
.mm = NULL, .active_mm = &init_mm,
其中init_mm被定义在init-mmc.c中
struct mm_struct init_mm = {
.mm_rb = RB_ROOT,
.pgd = swapper_pg_dir,
.mm_users = ATOMIC_INIT(2),
.mm_count = ATOMIC_INIT(1),
.mmap_sem = __RWSEM_INITIALIZER(init_mm.mmap_sem),
.page_table_lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(init_mm.page_table_lock),
.arg_lock = __SPIN_LOCK_UNLOCKED(init_mm.arg_lock),
.mmlist = LIST_HEAD_INIT(init_mm.mmlist),
.user_ns = &init_user_ns,
.cpu_bitmap = CPU_BITS_NONE,
INIT_MM_CONTEXT(init_mm)
};
3.3.2.2.2. 0号进程的演化
3.3.2.2.2.1. rest_init创建init和kthread进程
linux在无进程概念的情况下将一直从初始化部分的代码执行到 start_kernel ,然后再到其最后一个函数调用rest_init
大致是在vmlinux的入口startup_32(head.S)中为pid号为0的原始进程设置了执行环境,然后start_kernel完成内核的初始化工作,包括初始化页表,初始化中断向量表,初始化系统时间等
从 rest_init 开始,linux开始产生进程,因为Init_task是静态制造出来的,pid=0,它试图将从最早的汇编代码一直到start_kernel的执行都纳入到init_task的进程上下文中.
在这个函数中创建了init进程和kthreadd进程
noinline void __ref rest_init(void)
{
struct task_struct *tsk;
int pid;
rcu_scheduler_starting();
/*
* We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however
* the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if
* we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS.
*/
pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);
/*
* Pin init on the boot CPU. Task migration is not properly working
* until sched_init_smp() has been run. It will set the allowed
* CPUs for init to the non isolated CPUs.
*/
rcu_read_lock();
tsk = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpumask_of(smp_processor_id()));
rcu_read_unlock();
numa_default_policy();
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);
rcu_read_lock();
kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);
rcu_read_unlock();
/*
* Enable might_sleep() and smp_processor_id() checks.
* They cannot be enabled earlier because with CONFIG_PREEMPTION=y
* kernel_thread() would trigger might_sleep() splats. With
* CONFIG_PREEMPT_VOLUNTARY=y the init task might have scheduled
* already, but it's stuck on the kthreadd_done completion.
*/
system_state = SYSTEM_SCHEDULING;
complete(&kthreadd_done);
/*
* The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
* at least once to get things moving:
*/
schedule_preempt_disabled();
/* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
cpu_startup_entry(CPUHP_ONLINE);
}
pid = kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS);创建了1号内核线程,该线程最后转向用户空间,演变为init进程
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);创建了kthreadd内核线程
调用schedule函数切换当前进程,调用该函数后kernel_init将会运行
void __sched schedule_preempt_disabled(void)
{
sched_preempt_enable_no_resched();
schedule();
preempt_disable();
}
kernel_init会继续完成剩下的初始化工作,然后execve(/sbin/init),称为系统中其他进程的祖先
cpu_startup_entry函数调用cpu_idle_loop(),0号线程进入idle函数的循环,在该循环中周期性的检查
void cpu_startup_entry(enum cpuhp_state state)
{
arch_cpu_idle_prepare();
cpuhp_online_idle(state);
while (1)
do_idle();
}
3.3.2.2.2.2. idle的运行与调度
idle在系统没有其他就绪进程可执行的时候才会被调度,即执行 do_idle 函数
/*
* Generic idle loop implementation
*
* Called with polling cleared.
*/
static void do_idle(void)
{
int cpu = smp_processor_id();
/*
* If the arch has a polling bit, we maintain an invariant:
*
* Our polling bit is clear if we're not scheduled (i.e. if rq->curr !=
* rq->idle). This means that, if rq->idle has the polling bit set,
* then setting need_resched is guaranteed to cause the CPU to
* reschedule.
*/
__current_set_polling();
tick_nohz_idle_enter();
while (!need_resched()) {
rmb();
local_irq_disable();
if (cpu_is_offline(cpu)) {
tick_nohz_idle_stop_tick();
cpuhp_report_idle_dead();
arch_cpu_idle_dead();
}
arch_cpu_idle_enter();
/*
* In poll mode we reenable interrupts and spin. Also if we
* detected in the wakeup from idle path that the tick
* broadcast device expired for us, we don't want to go deep
* idle as we know that the IPI is going to arrive right away.
*/
if (cpu_idle_force_poll || tick_check_broadcast_expired()) {
tick_nohz_idle_restart_tick();
cpu_idle_poll();
} else {
cpuidle_idle_call();
}
arch_cpu_idle_exit();
}
/*
* Since we fell out of the loop above, we know TIF_NEED_RESCHED must
* be set, propagate it into PREEMPT_NEED_RESCHED.
*
* This is required because for polling idle loops we will not have had
* an IPI to fold the state for us.
*/
preempt_set_need_resched();
tick_nohz_idle_exit();
__current_clr_polling();
/*
* We promise to call sched_ttwu_pending() and reschedule if
* need_resched() is set while polling is set. That means that clearing
* polling needs to be visible before doing these things.
*/
smp_mb__after_atomic();
sched_ttwu_pending();
schedule_idle();
if (unlikely(klp_patch_pending(current)))
klp_update_patch_state(current);
}
默认的idle实现是hlt指令,hlt指令使cpu处于暂停状态,等待硬件中断发生的时候恢复,从而达到节能的目的.
rest_init 流程 |
说明 |
|---|---|
rcu_scheduler_starting |
|