7.9.2.2. 链表操作
7.9.2.2.1. 从尾到头打印链表
7.9.2.2.1.1. 题目描述
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
7.9.2.2.1.2. 解题思路
方法1: 先求链表长度,然后再将链表中元素逆序存入数组中
方法2: 先反转链表并求其长度,在将反转后的链表数据拷贝至数组中
7.9.2.2.1.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define USING_METHOD_1
//#define USING_METHOD_2
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};
#ifdef USING_METHOD_1
int *reversePrint(struct ListNode *head, int *returnSize)
{
int listlen= 0;
struct ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur)
{
listlen++;
cur = cur->next;
}
int *arr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * listlen);
*returnSize = listlen;
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
*(arr + listlen - 1) = cur->val;
cur = cur->next;
listlen--;
}
return arr;
}
#else
int *reversePrint(struct ListNode *head, int *returnSize)
{
int listlen = 0;
struct ListNode *cur = head;
struct ListNode *next = NULL;
struct ListNode *tail = NULL;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = tail;
tail = cur;
cur = next;
listlen++;
} //反转链表并求其长度
int *arr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*listlen);
*returnSize = listlen;
cur = tail;
for(int i = 0; i < listlen; i++)
{
arr[i] = cur->val;
cur = cur->next;
}
return arr;
}
#endif
void AddListNode(struct ListNode *head, struct ListNode *node)
{
struct ListNode * cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
return;
}
int main()
{
int listlen = 0;
int *arr;
static struct ListNode listhead = {.val = 20, .next = NULL};
struct ListNode node_1 = {.val = 30, .next = NULL};
struct ListNode node_2 = {.val = 40, .next = NULL};
struct ListNode node_3 = {.val = 50, .next = NULL};
struct ListNode node_4 = {.val = 60, .next = NULL};
struct ListNode node_5 = {.val = 70, .next = NULL};
AddListNode(&listhead, &node_1);
AddListNode(&listhead, &node_2);
AddListNode(&listhead, &node_3);
AddListNode(&listhead, &node_4);
AddListNode(&listhead, &node_5);
arr = reversePrint(&listhead, &listlen);
for(int i = 0; i < listlen; i++)
printf("%d\n", arr[i]);
return 0;
}
7.9.2.2.2. 删除链表的节点
7.9.2.2.2.1. 题目描述
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
返回删除后的链表的头节点。
示例
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
7.9.2.2.2.2. 题目解析
遍历链表,当head.val == val时,定位到目标节点
定位到目标节点后,需要修改这个节点,题目的要求是删除,对于链表中的每个节点来说,它都有前驱和后继两个节点,那么删除操作就很简单了:设节点 cur 的前驱节点为 pre ,后继节点为 cur.next ,执行 pre.next = cur.next ,即可实现删除 cur 节点。
7.9.2.2.2.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list_node
{
int value;
struct list_node* next;
};
int insert_listnode(struct list_node *head, struct list_node *node)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
return 0;
}
struct list_node* delete_listnode(struct list_node *head, int value)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->value == value)
{
if(cur == head)
{
return head->next;
}
prev->next = cur->next;
return head;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int traverse_listnode(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
unsigned int i = 0;
while(cur)
{
printf("list node %d ---> %d\n", i++, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int* ret = 0;
struct list_node node_0 = {.value = 10, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_1 = {.value = 3, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_2 = {.value = 2, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_3 = {.value = 8, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_4 = {.value = 0, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_5 = {.value = 5, .next = NULL};
struct list_node *head = &node_0;
insert_listnode(head, &node_1);
insert_listnode(head, &node_2);
insert_listnode(head, &node_3);
insert_listnode(head, &node_4);
insert_listnode(head, &node_5);
ret = delete_listnode(head, 10);
if(ret == NULL)
printf("not found list node\n");
else
head = ret;
traverse_listnode(head);
return 0;
}
7.9.2.2.3. 链表中倒数第 K 个节点
7.9.2.2.3.1. 题目描述
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第 k 个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从 1 开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第 1 个节点。
示例
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
7.9.2.2.3.2. 解析思路
1、初始化两个指针 fast 和 slow,一开始都指向链表的头节点 2、前指针 fast 先向前走 k 步 3、两个指针 fast 和 slow 同时向前移动,直到前指针slow 指向 NULL 4、最后返回 slow
7.9.2.2.3.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list_node
{
int value;
struct list_node* next;
};
int insert_listnode(struct list_node *head, struct list_node *node)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
return 0;
}
struct list_node* delete_listnode(struct list_node *head, int value)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->value == value)
{
if(cur == head)
{
return head->next;
}
prev->next = cur->next;
return head;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int traverse_listnode(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
unsigned int i = 0;
while(cur)
{
printf("list node %d ---> %d\n", i++, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct list_node* getKthFromEnd(struct list_node *head, int k)
{
struct list_node *fast = head;
struct list_node *slow = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
int main()
{
int* ret = 0;
struct list_node node_0 = {.value = 10, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_1 = {.value = 3, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_2 = {.value = 2, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_3 = {.value = 8, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_4 = {.value = 0, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_5 = {.value = 5, .next = NULL};
struct list_node *head = &node_0;
insert_listnode(head, &node_1);
insert_listnode(head, &node_2);
insert_listnode(head, &node_3);
insert_listnode(head, &node_4);
insert_listnode(head, &node_5);
struct list_node *new = getKthFromEnd(head, 3);
traverse_listnode(new);
return 0;
}
7.9.2.2.4. 反转链表
7.9.2.2.4.1. 题目描述
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
7.9.2.2.4.2. 题目解析
通过递归函数,一直递归到链表的最后一个结点为止,此时,该结点就是反转成功后的头结点,是最终的返回结果。
在递归函数中,让当前节点的下一个节点的 next 指针指向当前节点。
在递归函数中,让当前节点的 next 指针指向 null
通过二三步的操作,已经让递归函数中的链表实现了局部反转,将结果返回给上一层递归函数
所有递归结束后,链表反转成功。
7.9.2.2.4.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE 12
struct list_node
{
int value;
struct list_node *next;
};
int insert_listnode(struct list_node *head, struct list_node *node)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
return 0;
}
struct list_node* delete_listnode(struct list_node *head, int value)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->value == value)
{
if(cur == head)
{
return head->next;
}
prev->next = cur->next;
return head;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int traverse_listnode(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
unsigned int i = 0;
while(cur)
{
printf("list node %d ---> %d\n", i++, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct list_node* getKthFromEnd(struct list_node *head, int k)
{
struct list_node *fast = head;
struct list_node *slow = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct list_node* reverseList(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *tail = NULL, *next = NULL;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = tail;
tail = cur;
cur = next;
}
return tail;
}
struct list_node* reverseList_recusion(struct list_node *head)
{
if( head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
struct list_node *cur = reverseList_recusion(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return cur;
}
int main()
{
int* ret = 0;
struct list_node node_0 = {.value = 10, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_1 = {.value = 3, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_2 = {.value = 2, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_3 = {.value = 8, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_4 = {.value = 0, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_5 = {.value = 5, .next = NULL};
struct list_node *head = &node_0;
insert_listnode(head, &node_1);
insert_listnode(head, &node_2);
insert_listnode(head, &node_3);
insert_listnode(head, &node_4);
insert_listnode(head, &node_5);
//struct list_node *new = reverseList(head);
struct list_node *new = reverseList_recusion(head);
traverse_listnode(new);
return 0;
}
7.9.2.2.5. 复杂链表的复制
7.9.2.2.5.1. 题目描述
请实现 copyRandomList 函数,复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个节点除了有一个 next 指针指向下一个节点,还有一个 random 指针指向链表中的任意节点或者 null。
7.9.2.2.5.2. 题目解析
首先我得思路是创建一个新的链表,依次复制每个节点,但是问题出现了,random指向一个随机值,这个随机值可能没有创建呢,所以依次复制会出现错误。 random的复制成了难题。
假定现在有一个复杂链表的形状如下图:
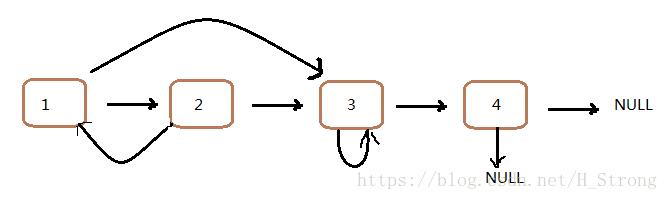
1.首先我们在每个链表节点的后面创建一个新的节点,将其串联起来。如下图的黄色箭头所示。
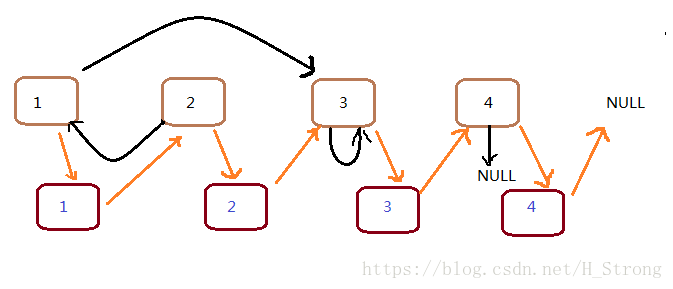
2.接下来,我们将它的新节点的random指向该指的地方,如下图的绿色箭头所示。
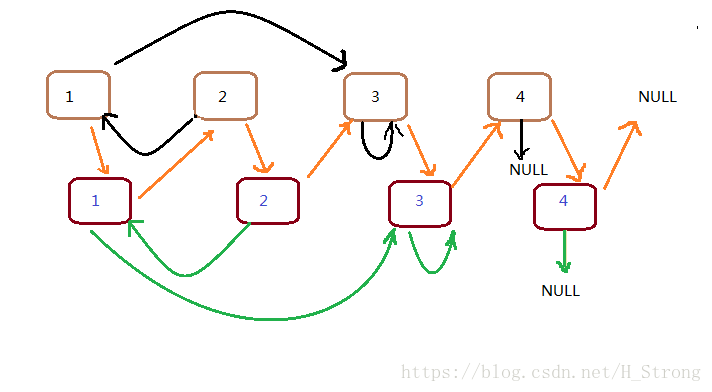
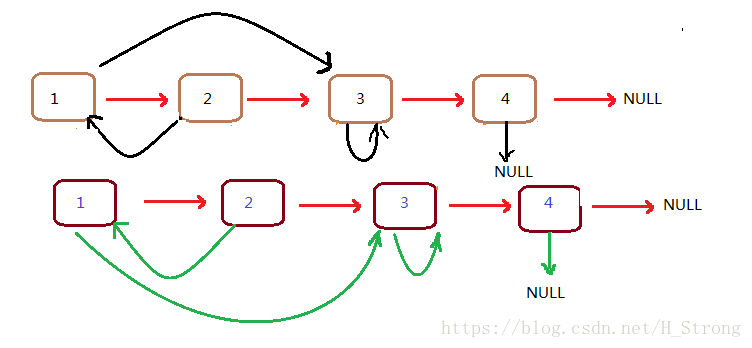
3.接下来我们把两个混在一起的链表拆开,拆开就可以变成两个链表。
7.9.2.2.5.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list_node
{
int value;
struct list_node *next;
struct list_node *random;
};
struct list_node* create_listnode(int value)
{
struct list_node *node = (struct list_node *)malloc(sizeof(struct list_node));
if(node != NULL)
{
node->value = value;
node->next = NULL;
node->random = NULL;
}
return node;
}
int traverse_listnode(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
unsigned int i = 0;
while(cur)
{
printf("list node %d ---> %d, list node random ---> %d\n", i++, cur->value, cur->random->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct list_node * copy_list(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *copy = NULL;
struct list_node *next = NULL;
struct list_node *new_list = NULL;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
copy = create_listnode(cur->value);
copy->next = next;
cur->next = copy;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->random != NULL)
{
copy = cur->next;
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
cur = head;
new_list = cur->next;
while(cur)
{
copy = cur->next;
next = cur->next->next;
cur->next = next;
copy->next = next ? next->next : NULL;
cur = next;
}
return new_list;
}
int main()
{
struct list_node *node0 = create_listnode(1);
struct list_node *node1 = create_listnode(3);
struct list_node *node2 = create_listnode(5);
struct list_node *node3 = create_listnode(9);
node0->next = node1;
node1->next = node2;
node2->next = node3;
node0->random = node3;
node1->random = node0;
node2->random = node1;
node3->random = node2;
//struct list_node *new = reverseList(head);
struct list_node *new = copy_list(node0);
traverse_listnode(new);
return 0;
}
7.9.2.2.6. 两个链表的第一个公共结点
7.9.2.2.6.1. 题目描述
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
7.9.2.2.6.2. 题目解析
无论 A、B 两个链表是否有相交点,最终都会指向一个相同的节点,要么是它们的公共尾部,要么是 NULL。
让指针 pointA 和 pointB 分别指向链表 A 和链表 B 的头结点,之后两个指针分别以步幅为 1 的速度向链表的尾部遍历。
当指针 pointA 遍历到链表 A 的尾节点时,此时指针 pointA 走了 a 个节点,将指针 pointA 指向链表 B 的头部,继续向后遍历,直至走到 c1,此时指针 pointA 总共走了 a + ( b - c ) 步。
当指针 pointB 遍历到链表 B 的尾节点时,此时指针 pointB 走了 b 个节点,将指针 pointB 指向链表 A 的头部,继续向后遍历,直至走到 c1,此时指针 pointB 总共走了 b + ( a - c ) 步。
根据数学知识,a + ( b - c ) = b + ( a - c ) ,如果 c > 0,表明两链表有公共尾部, c1 存在,两两链表同时到达 c1;如果 c = 0,表明两链表没有公共尾部,指针 pointA 和 pointB 都指向
7.9.2.2.6.3. 代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct list_node
{
int value;
struct list_node *next;
};
int insert_listnode(struct list_node *head, struct list_node *node)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
while(cur->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = node;
return 0;
}
struct list_node* delete_listnode(struct list_node *head, int value)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *prev = NULL;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->value == value)
{
if(cur == head)
{
return head->next;
}
prev->next = cur->next;
return head;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
int traverse_listnode(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
unsigned int i = 0;
while(cur)
{
printf("list node %d ---> %d\n", i++, cur->value);
cur = cur->next;
}
return 0;
}
struct list_node* getKthFromEnd(struct list_node *head, int k)
{
struct list_node *fast = head;
struct list_node *slow = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct list_node* reverseList(struct list_node *head)
{
struct list_node *cur = head;
struct list_node *tail = NULL, *next = NULL;
while(cur)
{
next = cur->next;
cur->next = tail;
tail = cur;
cur = next;
}
return tail;
}
struct list_node* reverseList_recusion(struct list_node *head)
{
if( head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
struct list_node *cur = reverseList_recusion(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return cur;
}
struct list_node* getIntersectionNode(struct list_node *head_1, struct list_node *head_2)
{
struct list_node *list_1 = head_1, *list_2 = head_2;
while(list_1 != list_2)
{
list_1 = list_1->next;
list_2 = list_2->next;
if(list_1 == NULL)
list_1 = head_2;
if(list_2 == NULL)
list_2 = head_1;
}
return list_1;
}
int main()
{
struct list_node node_0 = {.value = 10, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_1 = {.value = 3, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_2 = {.value = 2, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_3 = {.value = 8, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_4 = {.value = 0, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_5 = {.value = 5, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_6 = {.value = 15, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_7 = {.value = 12, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_8 = {.value = 3, .next = NULL};
struct list_node node_9 = {.value = 9, .next = NULL};
struct list_node *head = &node_0;
struct list_node *head_1 = &node_9;
insert_listnode(head, &node_1);
insert_listnode(head, &node_2);
insert_listnode(head, &node_3);
insert_listnode(head, &node_4);
insert_listnode(head, &node_5);
insert_listnode(head_1, &node_8);
insert_listnode(head_1, &node_7);
insert_listnode(head_1, &node_6);
insert_listnode(head_1, &node_3);
//struct list_node *new = reverseList(head);
struct list_node *new = getIntersectionNode(head, head_1);
printf("first intersetion node is %d\n", new->value);
return 0;
}