6.5.1. MP4文件格式
mp4标准.pdf
多媒体封装格式(也叫容器格式),是指按照一定的规则,将视频数据音频数据等放到一个文件中.常见的MKV,AVI,MP4都是封装格式.
MP4文件由多个box组成,每个box存储不同的信息,且box之间是树状结构
6.5.1.1. box
box类型有很多,下面是3种比较重要的顶层box:
ftyp: File Type Box, 描述文件遵从的MP4规范与版本
moov: Movie Box, 媒体的metadata信息,有且仅有一个
mdat: Media Data Box, 存放实际的媒体数据,一般有多个
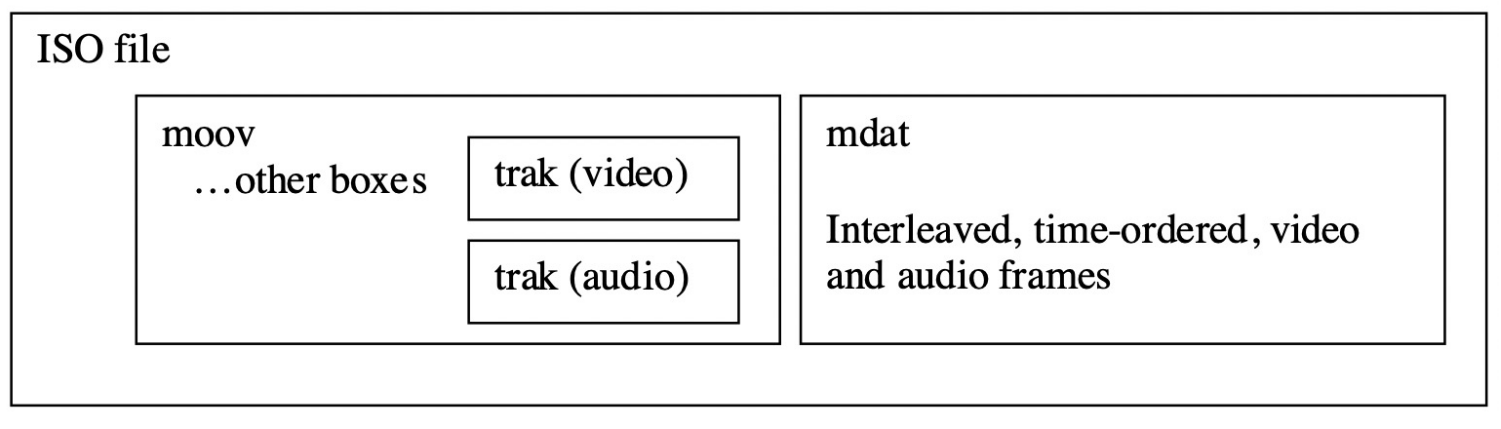
下面是常见的box

1个box由两部分组成,box header, box body
box header: box的元数据,比如box type, box size
box body: box的数据部分,实际存储的内容跟box类型有关,比如mdat中body部分存储的媒体数据
注解
box header中,只有type, size是必选字段.当size==0,存在largesize字段,在部分box中,还存在version,flags字段,这样的box叫full box. 当box body中嵌套其他box时,这样的box叫container box
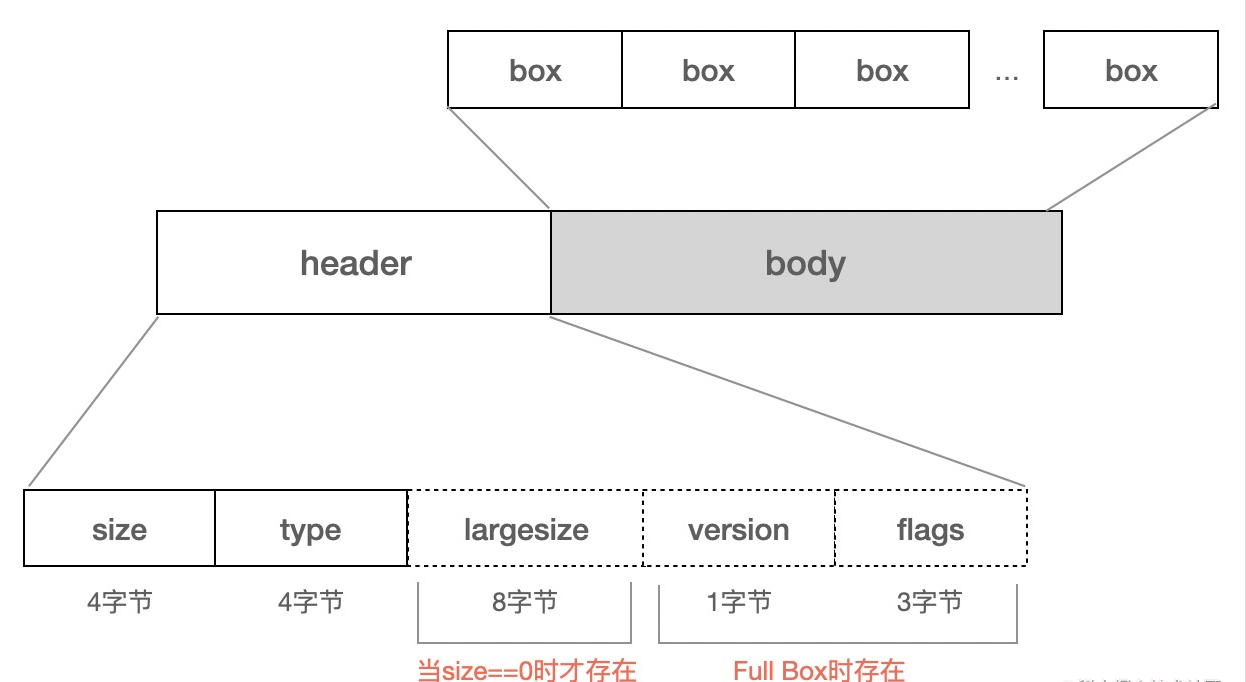
6.5.1.1.1. Box Header
字段定义如下
type: box类型,包括预定义类型,自定义扩展类型,占4个字节
预定义类型: 比如ftyp, moov, mdat等预定义好的类型
自定义扩展类型: 如果ttype == uuid,则表示自定义类型,size(或largesize)随后的16字节,为自定义的值
size: 包含box header在内的整个box的大小,单位是字节,当size为0或1时,需要特殊处理
size等于0: box的大小由后续的largesize确定(一般只有装载媒体数据的mdat box需要largesize)
size等于1: 当前box为文件的最后一个box,通常包含在mdat box中
largesize: box的大小,占8个字节
extended_type: 自定义扩展类型,占16个字节
version: 当前box的版本,为扩展做准备,占1个字节
flags: 标志位,占24位,具体含义由具体的box自己定义
box的伪代码:
aligned(8) class Box (unsigned int(32) boxtype, optional unsigned int(8)[16] extended_type) {
unsigned int(32) size;
unsigned int(32) type = boxtype;
if (size==1) {
unsigned int(64) largesize;
} else if (size==0) {
// box extends to end of file
}
if (boxtype==‘uuid’) {
unsigned int(8)[16] usertype = extended_type;
}
}
6.5.1.1.2. Box Body
box数据体,不同box包含的内容不同,需要参考具体box的定义
6.5.1.2. ftyp (File Type Box)
ftyp用来指出当前文件遵循的规范,ftyp的伪代码如下
aligned(8) class FileTypeBox
extends Box(‘ftyp’) {
unsigned int(32) major_brand;
unsigned int(32) minor_version;
unsigned int(32) compatible_brands[]; // to end of the box
}
major_brand: 比如常见的isom, mp41, avc1等.它表示最好基于哪种格式来解析当前的文件,如果major_brand是A, compatible_brands是A1,当解码器同时支持A,A1规范时最好使用A规范来解码当前媒体文件
minor_version: 提供major_brand的说明信息,比如版本号
compatible_brands: 文件兼容的brand列表
常见的几种brand如下
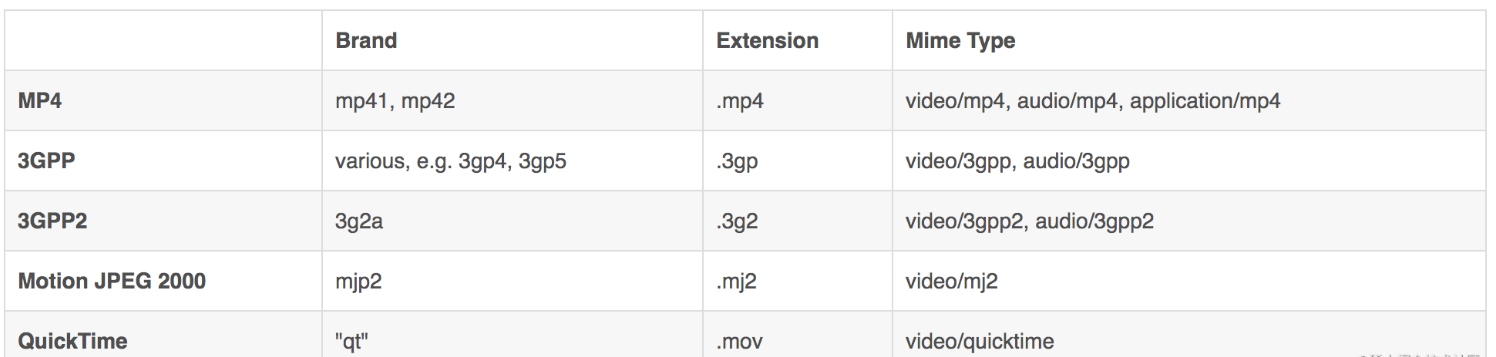
实例如下
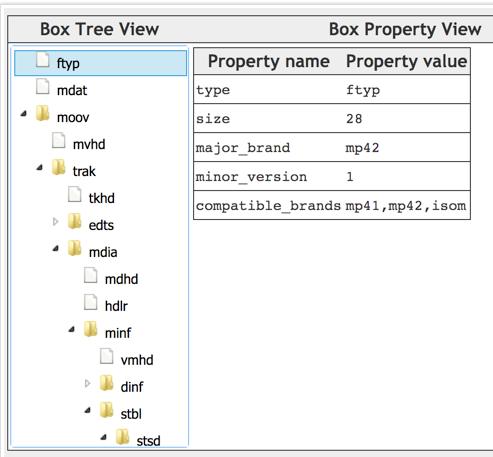
6.5.1.3. moov (Movie Box)
Movie Box,存储mp4的metadata,一般位于mp4文件的开头
moov中最重要的两个box是mvhd和trak:
mvhd: Movie Header Box, mp4文件的整理信息,如果创建时间,文件时长等
trak: Track Box, 一个mp4可以包含一个或多个轨道(比如视频轨道,音频轨道),轨道相关的信息就在trak中.trak是container box, 至少包含两个box(tkhd, media)
注解
mvhd针对整个影片,tkhd针对单个track, mdhd针对媒体,vmhd针对视频,smhd针对音频
6.5.1.3.1. mvhd (Movie Header Box)
MP4文件的整体信息,跟具体的视频流,音频流无关,比如创建时间,文件时长等
伪代码如下
aligned(8) class MovieHeaderBox
extends FullBox(‘mvhd’, version, 0) {
if (version==1) {
unsigned int(64) creation_time; //创建时间
unsigned int(64) modification_time; //文件修改时间
unsigned int(32) timescale; //一秒包含的时间单位
unsigned int(64) duration; //影片时长,根据文件中track的信息推导出来,等于时间最
//长的track的duration
} else { // version==0
unsigned int(32) creation_time;
unsigned int(32) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) timescale;
unsigned int(32) duration;
}
//推荐的播放速率,高低16位分别代码整数和小数部分
template int(32) rate = 0x00010000; // typically 1.0
//播放音量,高低8位分别代表整数小数部分,1.0为最大值
template int(16) volume = 0x0100; // typically, full volume const bit(16) reserved = 0
const unsigned int(32)[2] reserved = 0;
//视频的转换矩阵,一般忽略不计
template int(32)[9] matrix =
{ 0x00010000,0,0,0,0x00010000,0,0,0,0x40000000 };
// Unity matrix
bit(32)[6] pre_defined = 0;
//必须为非0值,当添加一个新的track id,必须比已经使用的track id要大
unsigned int(32) next_track_ID;
}
6.5.1.3.2. tkhd (Track Box)
单个track的metadata,伪代码如下
aligned(8) class TrackHeaderBox
extends FullBox(‘tkhd’, version, flags){
//flags: 按位或操作获得,默认值是7(0x000001 | 0x000002 | 0x000004)
//0x0000001:表示这个track是启用的,如果为0则表示这个track没有启用
//0x0000002:表示当前track在播放时会用到
//0x0000004:表示当前track用于预览模式
if (version==1) {
unsigned int(64) creation_time; //当前track创建时间
unsigned int(64) modification_time; //当前track的最近修改时间
unsigned int(32) track_ID; //当前track的唯一标识,不能为0,不能重复
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(64) duration; //当前track的完整时长(需要除以timescale得到具体秒数)
} else { // version==0
unsigned int(32) creation_time;
unsigned int(32) modification_time;
unsigned int(32) track_ID;
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(32) duration;
}
const unsigned int(32)[2] reserved = 0;
template int(16) layer = 0; //视频轨道的叠加顺序,数字越小越靠近观看者
template int(16) alternate_group = 0; //track的分组id,同一个分组里的track只能有一个处于播放状态
//音量值,介于0.0~1.0之间
template int(16) volume = {if track_is_audio 0x0100 else 0};
const unsigned int(16) reserved = 0;
template int(32)[9] matrix= { 0x00010000,0,0,0,0x00010000,0,0,0,0x40000000 }; // unity matrix
//视频的宽高
unsigned int(32) width;
unsigned int(32) height;
}
实例如下:
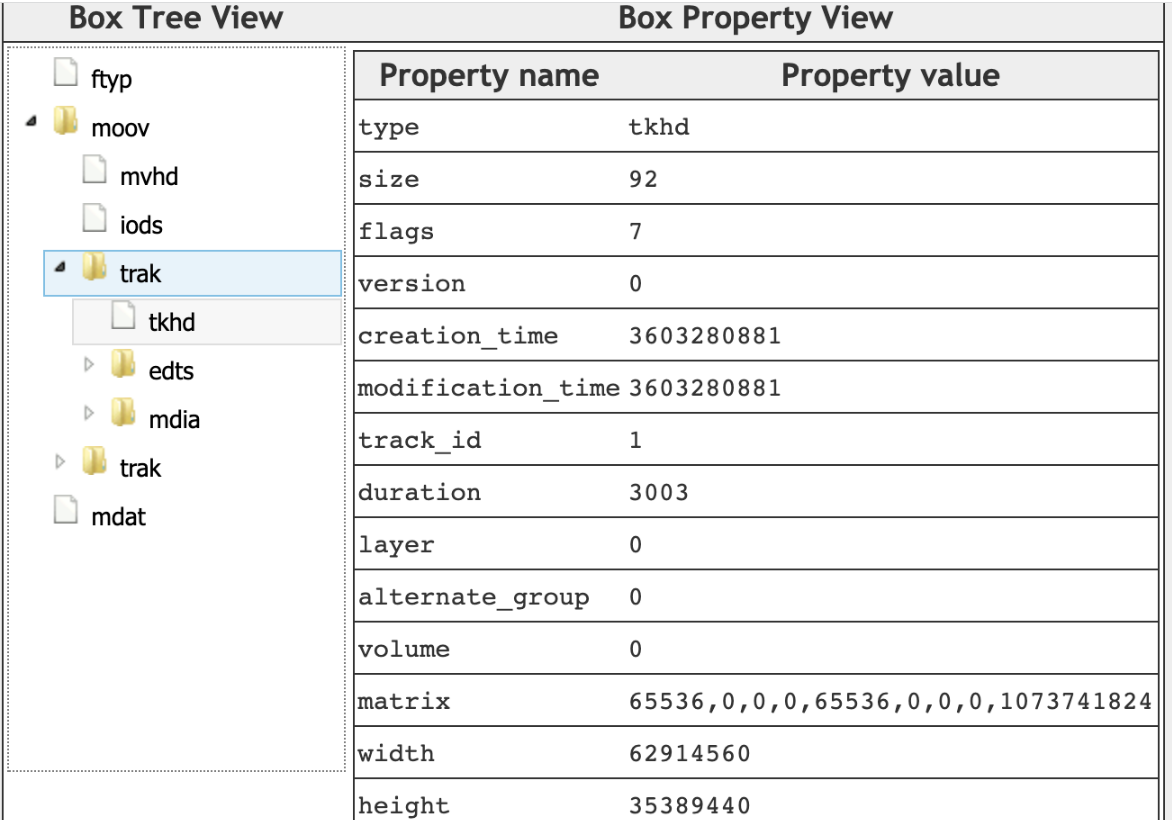
6.5.1.3.3. hdlr (Handler Reference Box)
hdlr申明当前track的类型,以及对应的处理器(handler)
handler_type的取值包括
vide(0x76 69 64 65),video track;
soun(0x73 6f 75 6e),audio track;
hint(0x68 69 6e 74),hint track;
伪代码如下:
aligned(8) class HandlerBox
extends FullBox(‘hdlr’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) pre_defined = 0;
unsigned int(32) handler_type;
const unsigned int(32)[3] reserved = 0;
string name; //utf8字符串,对handler进行描述
}
实例如下

6.5.1.3.4. stbl (Sample Table Box)
mp4文件的媒体数据在mdat box里,而stbl则包含了这些媒体数据的索引及时间信息.在mp4文件中,媒体数据被分成多个chunk,每个chunk可包含多个sample,而sample则由帧组成(通常一个 sample对应1帧)
stbl中比较关键的box包含stsd,stco,stsc,stsz,stss,ctts
stsd: 给出视频,音频的编码,宽高,音量等信息,以及每个sample中包含多少个frame
stco: chunk在文件中的偏移
stsc: 每个chunk中包含几个sample
stsz: 每个sample的size(单位是字节)
stts: 每个sample的时长
stss: 哪些sample是关键帧
ctts: 帧解码到渲染的时间差值,通常用在B帧的场景
stsd(Sample Description Box)
stsd给出sample的描述信息,这里面包含了在解码阶段需要用到的任意初始化信息,对于视频,音频来说所需的初始化信息不同,以下为视频部分的伪代码
aligned(8) abstract class SampleEntry (unsigned int(32) format)
extends Box(format){
const unsigned int(8)[6] reserved = 0;
unsigned int(16) data_reference_index;
//当mp4文件的数据部分被分割成多个片段,每个片段对应一个索引
}
// Visual Sequences
class VisualSampleEntry(codingname)
extends SampleEntry (codingname){
unsigned int(16) pre_defined = 0;
const unsigned int(16) reserved = 0;
unsigned int(32)[3] pre_defined = 0;
//视频宽高
unsigned int(16) width;
unsigned int(16) height;
//水平,垂直方向的分辨率
template unsigned int(32) horizresolution = 0x00480000; // 72 dpi
template unsigned int(32) vertresolution = 0x00480000; // 72 dpi
const unsigned int(32) reserved = 0;
//一个sample中包含多少个frame,对于video track来说,默认是1
template unsigned int(16) frame_count = 1;
//仅供参考的名字,通常用于展示,占32个字节,比如 AVC Coding
string[32] compressorname;
//位图的深度信息,如果0x0018(24)
template unsigned int(16) depth = 0x0018;
int(16) pre_defined = -1;
}
// AudioSampleEntry、HintSampleEntry 定义略过
aligned(8) class SampleDescriptionBox (unsigned int(32) handler_type)
extends FullBox('stsd', 0, 0){
int i ;
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i = 1 ; i u entry_count ; i++) {
switch (handler_type){
case ‘soun’: // for audio tracks
AudioSampleEntry();
break;
case ‘vide’: // for video tracks
VisualSampleEntry();
break;
case ‘hint’: // Hint track
HintSampleEntry();
break;
}
}
}
实例如下
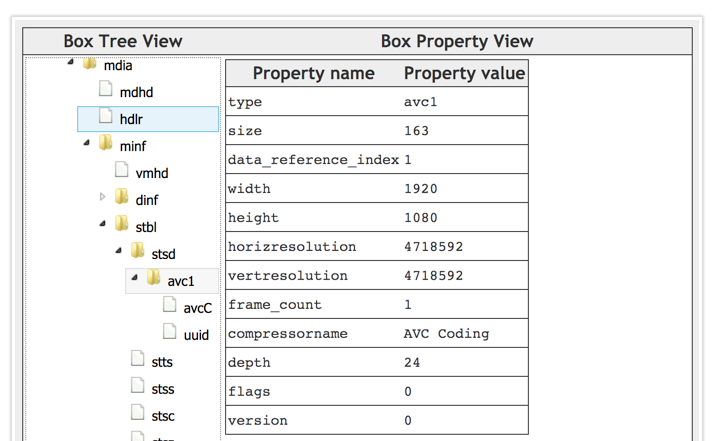
stco(Chunk Offset Box)
chunk在文件中的偏移量,针对小文件,大文件,有两种不同的box类型,分别是stco,co64,他们的结构是一样的,只是字段长度不同
chunk_offset指的是在文件本身中的offset,而不是某个box的内部偏移.在构建mp4文件的时候,需要特别注意moov所处的位置,它对于chunk_offset的值是有影响的
stco的伪代码如下
# Box Type: ‘stco’, ‘co64’
# Container: Sample Table Box (‘stbl’) Mandatory: Yes
# Quantity: Exactly one variant must be present
aligned(8) class ChunkOffsetBox
extends FullBox(‘stco’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) chunk_offset;
}
}
aligned(8) class ChunkLargeOffsetBox
extends FullBox(‘co64’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(64) chunk_offset;
}
}
实例如下

stsc(Sample To Chunk Box)
sample以chunk为单位分成多个组,chunk的size可以是不同的,chunk里面的sample的size也可以是不同的
aligned(8) class SampleToChunkBox
extends FullBox(‘stsc’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count; //有多少个表项
for (i=1; i u entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) first_chunk; //当前表项中对应的第一个chunk的序号
unsigned int(32) samples_per_chunk; //每个chunk包含的sample数
unsigned int(32) sample_description_index; //指向stsd中的sample description的索引值
}
}
实例
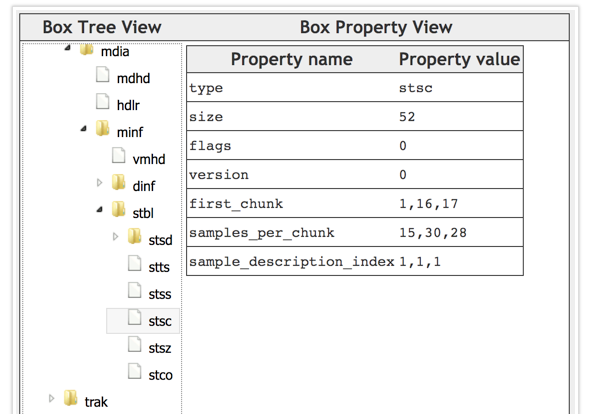
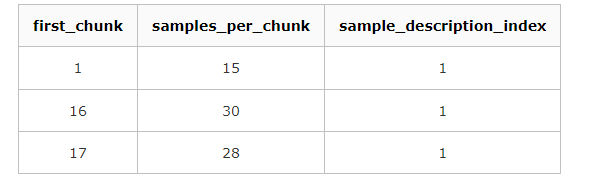
1.需要1~15的chunk,每个chunk包含15个sample
2.需要为16的chunk,包含30个sample
3.需要为17及以后的chunk,每个chunk包含28个sample
4.以上所有chunk中的sample,对应的sample description的索引都是1
stsz(Sample Size Boxes)
每个sample的大小,根据sample_size的字段可以知道当前track包含了多少个sample(或帧), 有两种不同的box类型,stsz, stz2
aligned(8) class SampleSizeBox
extends FullBox(‘stsz’, version = 0, 0) {
//通常为0,如果sample_size不为0,所有的sample都是同样的大小,如果sample_size为0,sample的大小可能不一样
unsigned int(32) sample_size;
//当前track里面的sample数目
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
if (sample_size==0) {
for (i=1; i u sample_count; i++) {
//单个sample的大小
unsigned int(32) entry_size;
}
}
}
示例
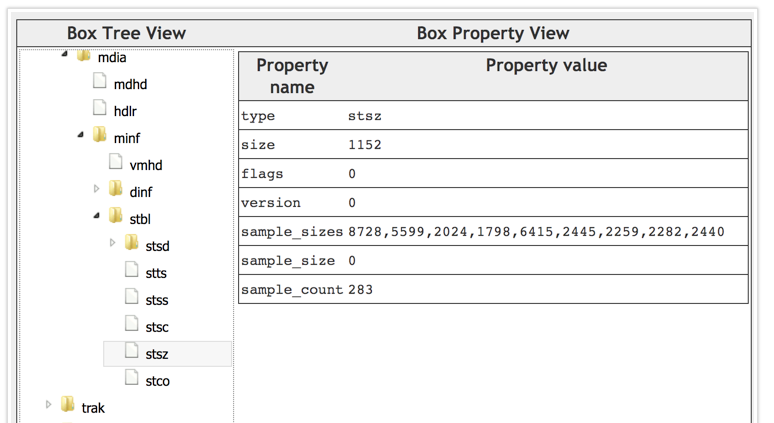
stts(Decoding Time to Sample Box)
stts包含dts到sample number的映射表,主要用来推导每个帧的时长
aligned(8) class TimeToSampleBox
extends FullBox(’stts’, version = 0, 0) {
//stts中包含的entry条目数
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_count;//单个entry中具有相同时长的连续sample的个数
unsigned int(32) sample_delta;//sample的时长(以timescale为计量)
}
}
实例
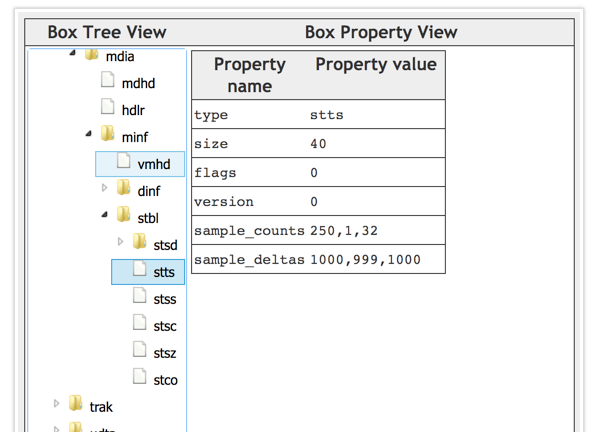
entry_count为3,前250个sample时长为1000,第251个sample时长为999,第252~283个sample的时长为1000
如果timesacle为1000,则实际时长需要除以1000
stss(Sync Sample Box)
mp4文件中,关键帧所在的sample的序号,如果没有stss的话,所有sample中都是关键帧
aligned(8) class SyncSampleBox
extends FullBox(‘stss’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count; //entry的条目数,可以认为是关键帧的数目
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_number; //关键帧对应的sample序号(从1开始计算)
}
}
实例
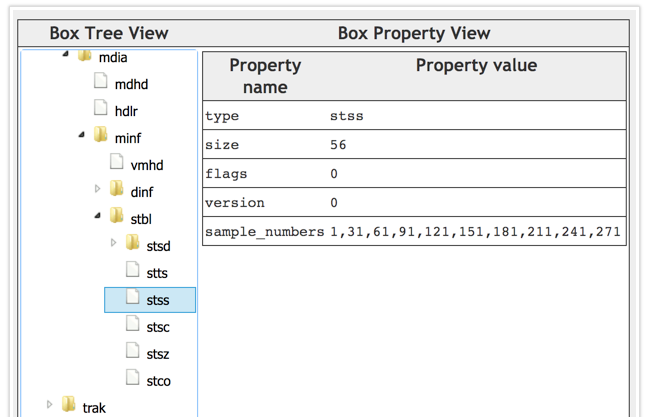
第1、31、61、91、121…271个sample是关键帧。
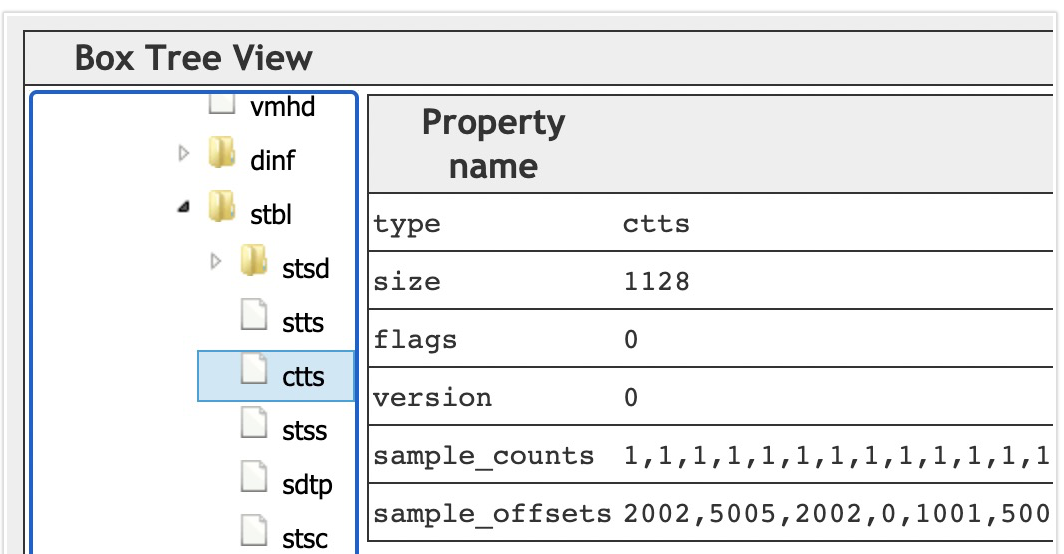
ctts(Composition Time to Sample Box)
从解码(dts)到渲染(pts)之间的差值. 对于只有I帧,P帧的视频来说,解码顺序,渲染顺序是一致的,此时ctts没必要存在. 对应存在B帧的视频来说,ctts就需要存在来,当pts, dts不像等时,就需要ctts了.公式为 CT(n) = DT(n) + CTTS(n)
aligned(8) class CompositionOffsetBox
extends FullBox(‘ctts’, version = 0, 0) {
unsigned int(32) entry_count;
int i;
for (i=0; i < entry_count; i++) {
unsigned int(32) sample_count;
unsigned int(32) sample_offset;
}
}
示例